No products in the cart.
- Latest
- Trending
ADVERTISEMENT
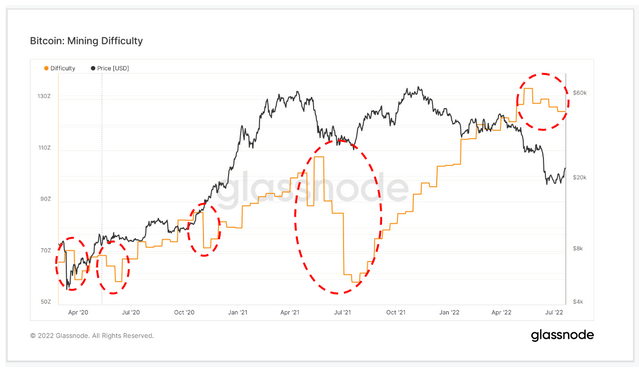
According to an analysis performed by CryptoSlate using Glassnode data, the difficulty of Bitcoin (BTC) mining will be adjusted downward by about 4.5% in the next adjustment window around 7 pm on July 21st. Expected.
The event shows that mining will be the least difficult after China cracked down on Proof-of-Work (PoW) mining in May 2021. research It was suggested that 75% of the hash rate of the network is from China.
The graph below shows the past four cases of significant downward revisions. These occurred in March 2020, May 2020, October 2020, and July 2021, with the July adjustment being the biggest drop.
The Hash ribbon indicator Identify the pain of Bitcoin miners. This means that the mining cost of BTC is too high compared to its price. High distress indicates the surrender of miners and in some cases may indicate the bottom of the market.
The graph below shows the 60-day and 30-day hash rate moving averages (MA) and BTC prices. When the 30-day moving average exceeds the 60-day moving average, the ribbon turns dark red, suggesting a possible surrender (miner gives up) and bottom, indicating a bullish scenario.
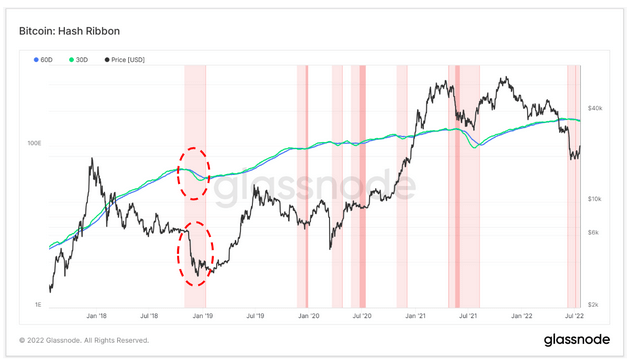
Similarly, when the 60-day moving average exceeds the 30-day moving average, the ribbon turns bright red, creating a bearish scenario.
The current miner’s surrender stage has continued for the past 42 days. During the 2018 bear cycle, the surrender lasted 72 days, and after the surrender was over, BTC recorded a 300% profit and peaked at $ 12,000.
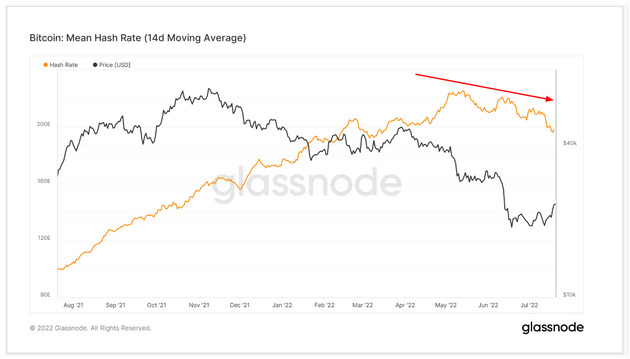
Since July 2021, following China’s ban, hash rates have formed a rounded top pattern. This suggests that weak miners are still in captivity, leaving strong miners to mine in a less competitive environment.
Average hash rate It refers to the average estimated number of hashes per second resulting from the efforts of miners. Often this is a measure of security and is considered an approximation of the number of miners supporting the network.
Bitcoin’s hash rate peaked in May, leading to a decisive downtrend. When used in combination with hash ribbon data, this supports the theory that weak miners exist, leaving the most efficient miners to support the network.
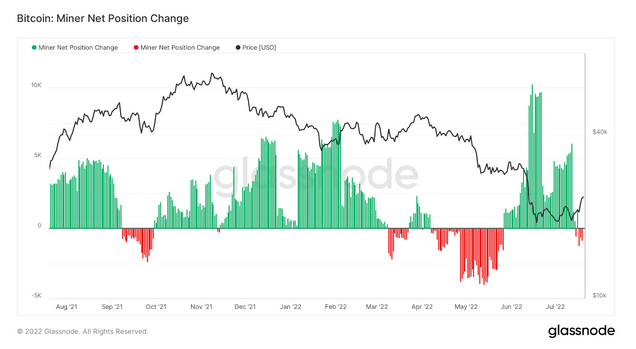
Changes in the net position of Bitcoin miners refer to the rate of change in unused supply. Positive flow indicates that the miner holds more tokens than it sells accumulation.
Currently, miners are in a modest distribution stage, and miners are selling their holdings, mainly due to various factors such as market conditions, operating pressure, energy costs, and unprofitable old mining equipment. Suggests. However, the magnitude of the change in the current net negative position is small compared to past cases where this happened.
In a recent tweet, Jason Williams, the author of Bitcoin: Hard money you can’t F * ck posted about the nine stages of mining that ended up with rising BTC prices.
Short mining thread
Bitcoin’s programmatic monetary policy is a very cool feature. Watch it work over the next four weeks.
1. Bitcoin price cut
2. Miners turn off ASICS due to inefficiency.
3. Hash rate drops
4. Difficulty goes downJason A. Williams (@GoingParabolic) June 16, 2022
5. Bitcoin rewards for efficiency improvement
6. Efficient miners buy cheap ASICS
7. Hash rate will increase
8. Difficulty goes up
9. BTC price increaseJason A. Williams (@GoingParabolic) June 16, 2022
On-chain metrics show that the market is currently in stage 4-mining difficulty is diminishing. In the coming weeks, on-chain data may show an increase in hash rates and the difficulty of returning upwards.
The miner’s surrender is still underway, but the amount of BTC transferred from the miner to the exchange suggests that the miner’s pain is chilling.
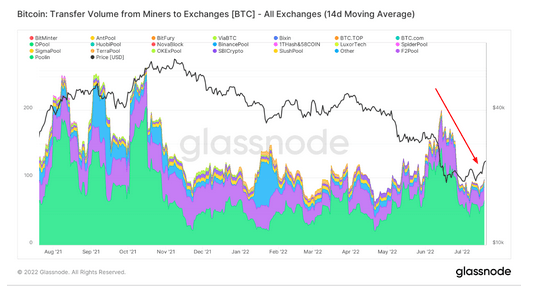
An important factor to consider is the end of the surrender phase, but it involves macroeconomic factors, including the outcome of the July 27 FOMC meeting.
Become a member of CryptoSlate Edge and access our exclusive Discord community, more exclusive content and analytics.
On-chain analysis
Price snapshot
Other contexts
Join now for $ 19 per month Explore all the benefits
Copyright © Pbird Media | Copyright © All rights reserved 2024

Copyright © Pbird Media | Copyright © All rights reserved 2024